AC & DC charging refers to the two types of electrical currents that can be used to fuel electric vehicles. The AC comes from the grid and will typically be converted into DC via a converter (onboard charger) within the vehicle. It’s important to understand the difference between the two and the advantages & disadvantages of both to choose the most suitable product for your needs.
AC (Alternating Current) Charging
An AC charger uses power from the grid, supplied in alternating current, which is then converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard charger before it is sent to the car’s battery. This means charging speeds can be limited depending on how fast the onboard system can receive and convert the alternating current.
DC (Direct Current) Charging
A DC charger supplies power directly to the battery management system (BMS) inside the vehicle, with no onboard charging infrastructure needed inside the vehicle. Using a DC charger means bypassing the onboard charger Higher power can be supplied meaning charging times can be considerably faster.
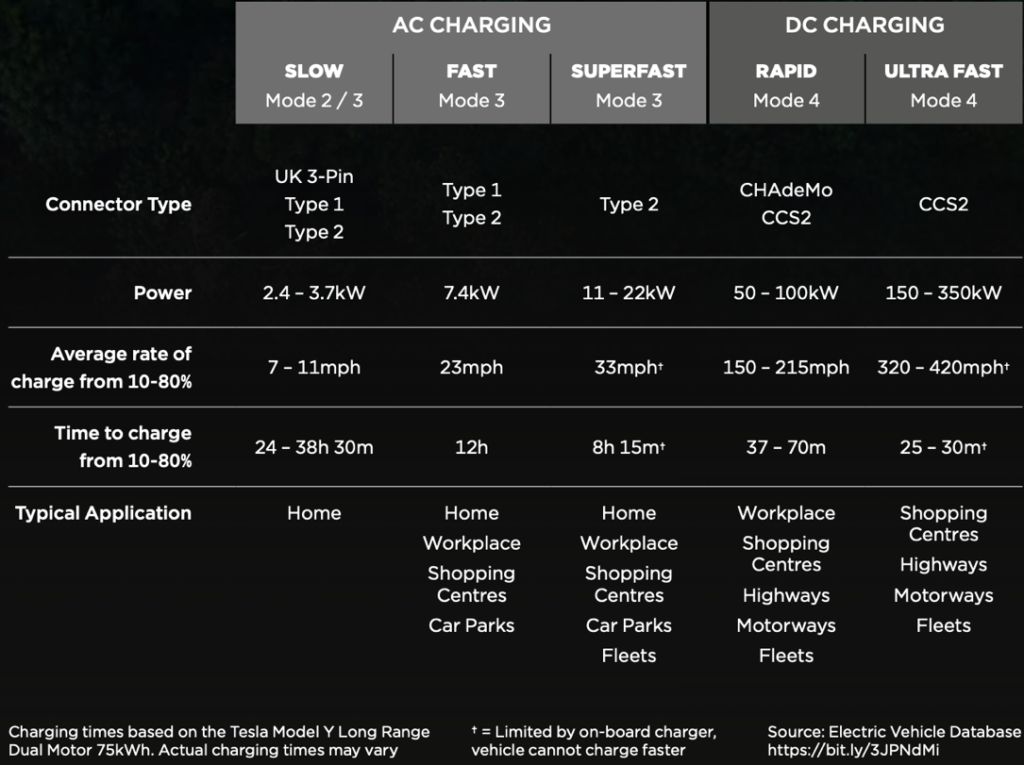
AC vs. DC Charging Comparisons
If you think you could benefit from the Rolec EV ChargePoint at your home or business, get in touch with us to begin your ChargePoint installation process with EV Charging Company.
Let EV Charging Company help you start your EV journey today. Contact our team of experts on 01625 569574 or email [email protected]